Detailed Description
Back to list of all libraries | See all modules
Library mrpt-tfest
Transformation estimation (tfest): This module provides functions in charge of solving the optimization problem of aligning a set of 2D or 3D corresponding points, estimating the optimal transformation between the two frames of reference.
Note that this does not include the related iterative ICP algorithm (see mrpt::slam::CICP), included in the library [mrpt-slam]
See list of all functions: mrpt::tfest
Classes | |
| struct | mrpt::tfest::TPotentialMatch |
| For each individual-compatibility (IC) test, the indices of the candidate match between elements in both reference frames. More... | |
| struct | mrpt::tfest::TSE2RobustParams |
| Parameters for se2_l2_robust(). More... | |
| struct | mrpt::tfest::TSE2RobustResult |
| Output placeholder for se2_l2_robust() More... | |
| struct | mrpt::tfest::TSE3RobustParams |
| Parameters for se3_l2_robust(). More... | |
| struct | mrpt::tfest::TSE3RobustResult |
| Output placeholder for se3_l2_robust() More... | |
Namespaces | |
| mrpt::tfest | |
| Functions for estimating the optimal transformation between two frames of references given measurements of corresponding points. | |
Typedefs | |
| using | mrpt::tfest::TFunctorCheckPotentialMatch = std::function< bool(const TPotentialMatch &)> |
Functions | |
| bool | mrpt::tfest::se2_l2 (const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList &in_correspondences, mrpt::math::TPose2D &out_transformation, mrpt::math::CMatrixDouble33 *out_estimateCovariance=nullptr) |
| Least-squares (L2 norm) solution to finding the optimal SE(2) (x,y,yaw) between two reference frames. More... | |
| bool | mrpt::tfest::se2_l2 (const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList &in_correspondences, mrpt::poses::CPosePDFGaussian &out_transformation) |
| bool | mrpt::tfest::se2_l2_robust (const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList &in_correspondences, const double in_normalizationStd, const TSE2RobustParams &in_ransac_params, TSE2RobustResult &out_results) |
| Robust least-squares (L2 norm) solution to finding the optimal SE(2) (x,y,yaw) between two reference frames. More... | |
| bool | mrpt::tfest::se3_l2 (const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList &in_correspondences, mrpt::poses::CPose3DQuat &out_transform, double &out_scale, bool forceScaleToUnity=false) |
| Least-squares (L2 norm) solution to finding the optimal SE(3) transform between two reference frames using the "quaternion" or Horn's method: More... | |
| bool | mrpt::tfest::se3_l2 (const std::vector< mrpt::math::TPoint3D > &in_points_this, const std::vector< mrpt::math::TPoint3D > &in_points_other, mrpt::poses::CPose3DQuat &out_transform, double &out_scale, bool forceScaleToUnity=false) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.This version accepts corresponding points as two vectors of TPoint3D (must have identical length). More... | |
| bool | mrpt::tfest::se3_l2_robust (const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList &in_correspondences, const TSE3RobustParams &in_params, TSE3RobustResult &out_results) |
| Least-squares (L2 norm) solution to finding the optimal SE(3) transform between two reference frames using RANSAC and the "quaternion" or Horn's method: More... | |
Typedef Documentation
◆ TFunctorCheckPotentialMatch
| using mrpt::tfest::TFunctorCheckPotentialMatch = typedef std::function<bool(const TPotentialMatch&)> |
Definition at line 31 of file indiv-compat-decls.h.
Function Documentation
◆ se2_l2() [1/2]
| bool mrpt::tfest::se2_l2 | ( | const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList & | in_correspondences, |
| mrpt::math::TPose2D & | out_transformation, | ||
| mrpt::math::CMatrixDouble33 * | out_estimateCovariance = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Least-squares (L2 norm) solution to finding the optimal SE(2) (x,y,yaw) between two reference frames.
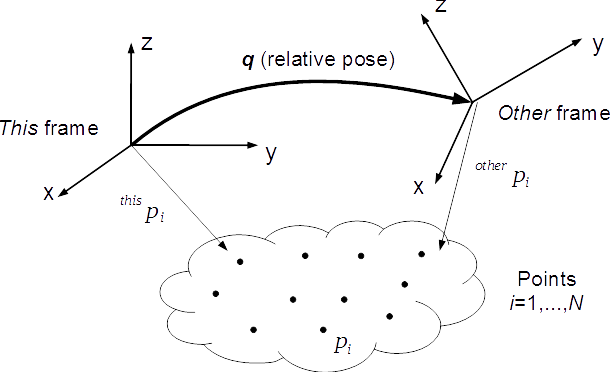
The optimal transformation q fulfills  , that is, the transformation of frame
, that is, the transformation of frame other with respect to this.
- Parameters
-
[in] in_correspondences The set of correspondences. [out] out_transformation The pose that minimizes the mean-square-error between all the correspondences. [out] out_estimateCovariance If provided (!=nullptr) this will contain on return a 3x3 covariance matrix with the NORMALIZED optimal estimate uncertainty. This matrix must be multiplied by 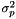 , the variance of matched points in
, the variance of matched points in 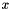 and
and 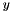 (see paper http://www.mrpt.org/Paper:Occupancy_Grid_Matching)
(see paper http://www.mrpt.org/Paper:Occupancy_Grid_Matching)
- Returns
- True if there are at least two correspondences, or false if one or none, thus we cannot establish any correspondence.
- See also
- robustRigidTransformation
- Note
- Reference for covariance calculation: J.L. Blanco, J. Gonzalez-Jimenez, J.A. Fernandez-Madrigal, "A Robust, Multi-Hypothesis Approach to Matching Occupancy Grid Maps", Robotica, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0263574712000732
- [New in MRPT 1.3.0] This function replaces mrpt::scanmatching::leastSquareErrorRigidTransformation()
- This function is hand-optimized for SSE2 architectures (if SSE2 is enabled from CMake)
- See also
- se3_l2, se2_l2_robust
Definition at line 46 of file se2_l2.cpp.
References MRPT_END, MRPT_START, mrpt::math::TPose2D::phi, mrpt::math::square(), mrpt::math::TPose2D::x, and mrpt::math::TPose2D::y.
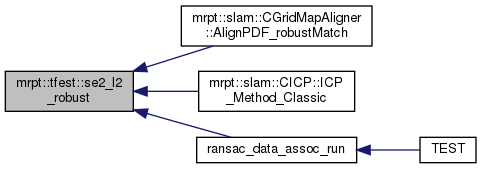
Referenced by mrpt::slam::CGridMapAligner::AlignPDF_robustMatch(), mrpt::slam::CICP::ICP_Method_Classic(), ransac_data_assoc_run(), mrpt::tfest::se2_l2(), and mrpt::tfest::se2_l2_robust().

◆ se2_l2() [2/2]
| bool mrpt::tfest::se2_l2 | ( | const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList & | in_correspondences, |
| mrpt::poses::CPosePDFGaussian & | out_transformation | ||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
Definition at line 28 of file se2_l2.cpp.
References mrpt::poses::CPosePDFGaussian::cov, mrpt::poses::CPosePDFGaussian::mean, and mrpt::tfest::se2_l2().

◆ se2_l2_robust()
| bool mrpt::tfest::se2_l2_robust | ( | const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList & | in_correspondences, |
| const double | in_normalizationStd, | ||
| const TSE2RobustParams & | in_ransac_params, | ||
| TSE2RobustResult & | out_results | ||
| ) |
Robust least-squares (L2 norm) solution to finding the optimal SE(2) (x,y,yaw) between two reference frames.
This method implements a RANSAC-based robust estimation, returning a probability distribution over all the posibilities as a Sum of Gaussians.
The optimal transformation q fulfills 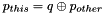 , that is, the transformation of frame
, that is, the transformation of frame other with respect to this.

The technique was described in the paper:
- J.L. Blanco, J. Gonzalez-Jimenez, J.A. Fernandez-Madrigal, "A Robust, Multi-Hypothesis Approach to Matching Occupancy Grid Maps", Robotica, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0263574712000732
This works as follows:
Repeat "ransac_nSimulations" times:
- Randomly pick TWO correspondences from the set "in_correspondences".
- Compute the associated rigid transformation.
- For "ransac_maxSetSize" randomly selected correspondences, test for "consensus" with the current group:
- If if is compatible (ransac_mahalanobisDistanceThreshold), grow the "consensus set"
- If not, do not add it.
For more details refer to the tutorial on scan matching methods.
- Parameters
-
[in] in_normalizationStd The standard deviation (not variance) of landmarks/points/features being matched in X,Y. Used to normalize covariances returned as the SoG. (Refer to paper)
NOTE: Parameter
ransac_maxSetSizeshould be set toin_correspondences.size()to make sure that every correspondence is tested for each random permutation.
- Returns
- True upon success, false if no subset was found with the minimum number of correspondences.
- Note
- [New in MRPT 1.3.0] This function replaces mrpt::scanmatching::robustRigidTransformation()
- See also
- se3_l2, se2_l2_robust
Definition at line 78 of file se2_l2_ransac.cpp.
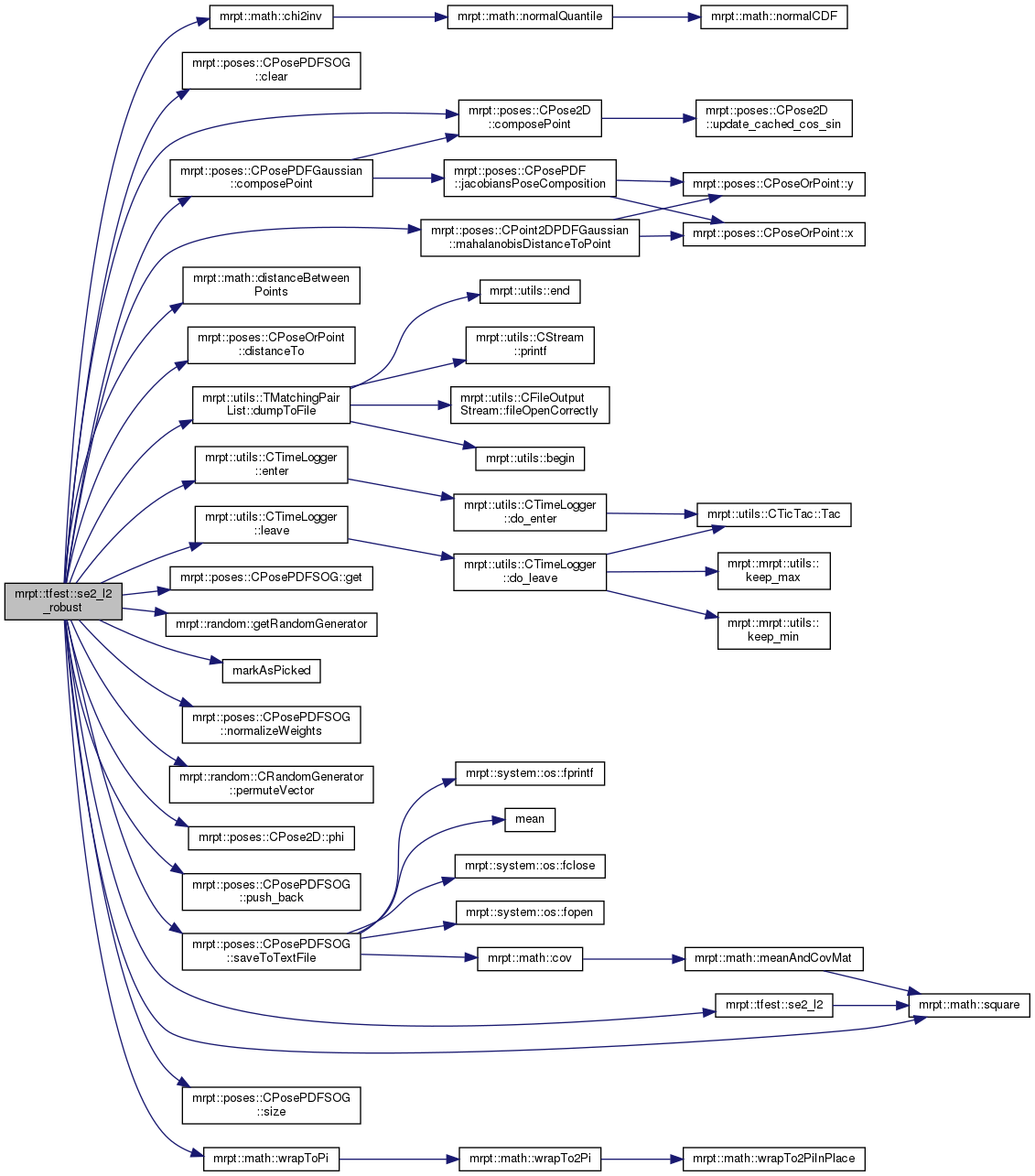
References ASSERT_, mrpt::math::chi2inv(), mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::clear(), mrpt::poses::CPose2D::composePoint(), mrpt::poses::CPosePDFGaussian::composePoint(), mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::TGaussianMode::cov, mrpt::poses::CPosePDFGaussian::cov, DEG2RAD, mrpt::math::distanceBetweenPoints(), mrpt::poses::CPoseOrPoint< DERIVEDCLASS >::distanceTo(), mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList::dumpToFile(), mrpt::utils::CTimeLogger::enter(), mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::get(), mrpt::random::getRandomGenerator(), mrpt::tfest::TPotentialMatch::idx_other, mrpt::tfest::TPotentialMatch::idx_this, mrpt::tfest::TSE2RobustResult::largestSubSet, mrpt::utils::CTimeLogger::leave(), mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::TGaussianMode::log_w, mrpt::poses::CPoint2DPDFGaussian::mahalanobisDistanceToPoint(), markAsPicked(), mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::TGaussianMode::mean, mrpt::poses::CPosePDFGaussian::mean, min, MRPT_END_WITH_CLEAN_UP, MRPT_START, normalizationStd, mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::normalizeWeights(), mrpt::utils::TMatchingPair::other_idx, mrpt::utils::TMatchingPair::other_x, mrpt::utils::TMatchingPair::other_y, mrpt::random::CRandomGenerator::permuteVector(), mrpt::poses::CPose2D::phi(), mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::push_back(), mrpt::tfest::TSE2RobustResult::ransac_iters, mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::saveToTextFile(), mrpt::tfest::se2_l2(), mrpt::poses::CPosePDFSOG::size(), mrpt::math::square(), mrpt::utils::TMatchingPair::this_idx, mrpt::utils::TMatchingPair::this_x, mrpt::utils::TMatchingPair::this_y, mrpt::tfest::TSE2RobustResult::transformation, and mrpt::math::wrapToPi().
Referenced by mrpt::slam::CGridMapAligner::AlignPDF_robustMatch(), mrpt::slam::CICP::ICP_Method_Classic(), and ransac_data_assoc_run().
◆ se3_l2() [1/2]
| bool mrpt::tfest::se3_l2 | ( | const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList & | in_correspondences, |
| mrpt::poses::CPose3DQuat & | out_transform, | ||
| double & | out_scale, | ||
| bool | forceScaleToUnity = false |
||
| ) |
Least-squares (L2 norm) solution to finding the optimal SE(3) transform between two reference frames using the "quaternion" or Horn's method:
- "Closed-form solution of absolute orientation using unit quaternions", BKP Horn, Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1987.
The optimal transformation q fulfills 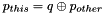 , that is, the transformation of frame
, that is, the transformation of frame other with respect to this.

- Parameters
-
[in] in_correspondences The coordinates of the input points for the two coordinate systems "this" and "other" [out] out_transform The output transformation [out] out_scale The computed scale of the optimal transformation (will be 1.0 for a perfectly rigid translation + rotation). [in] forceScaleToUnity Whether or not force the scale employed to rotate the coordinate systems to one (rigid transformation)
- Note
- [New in MRPT 1.3.0] This function replaces mrpt::scanmatching::leastSquareErrorRigidTransformation6DRANSAC() and mrpt::scanmatching::HornMethod()
- See also
- se2_l2, se3_l2_robust
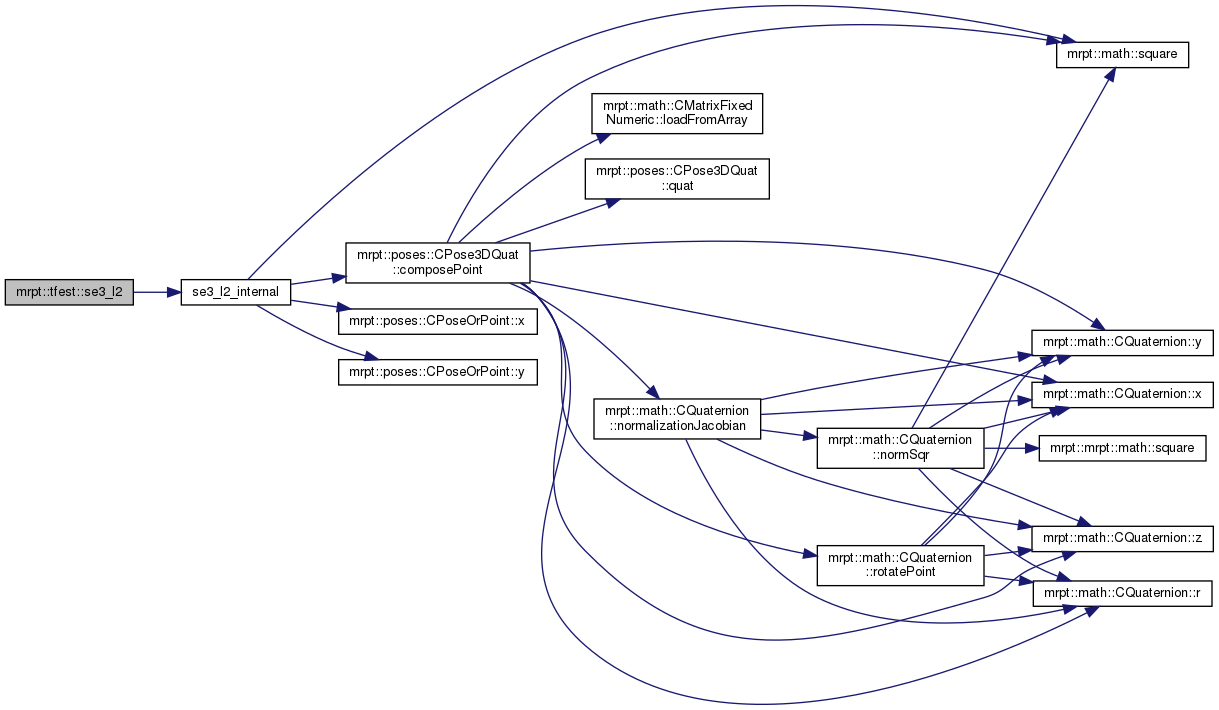
Definition at line 223 of file se3_l2.cpp.
References se3_l2_internal().
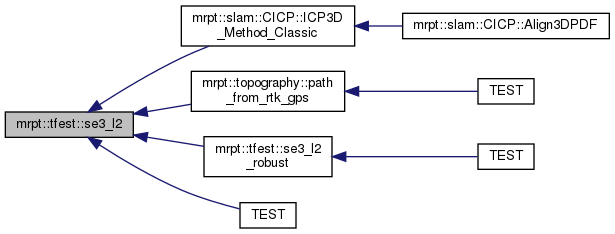
Referenced by mrpt::slam::CICP::ICP3D_Method_Classic(), mrpt::topography::path_from_rtk_gps(), mrpt::tfest::se3_l2_robust(), and TEST().

◆ se3_l2() [2/2]
| bool mrpt::tfest::se3_l2 | ( | const std::vector< mrpt::math::TPoint3D > & | in_points_this, |
| const std::vector< mrpt::math::TPoint3D > & | in_points_other, | ||
| mrpt::poses::CPose3DQuat & | out_transform, | ||
| double & | out_scale, | ||
| bool | forceScaleToUnity = false |
||
| ) |
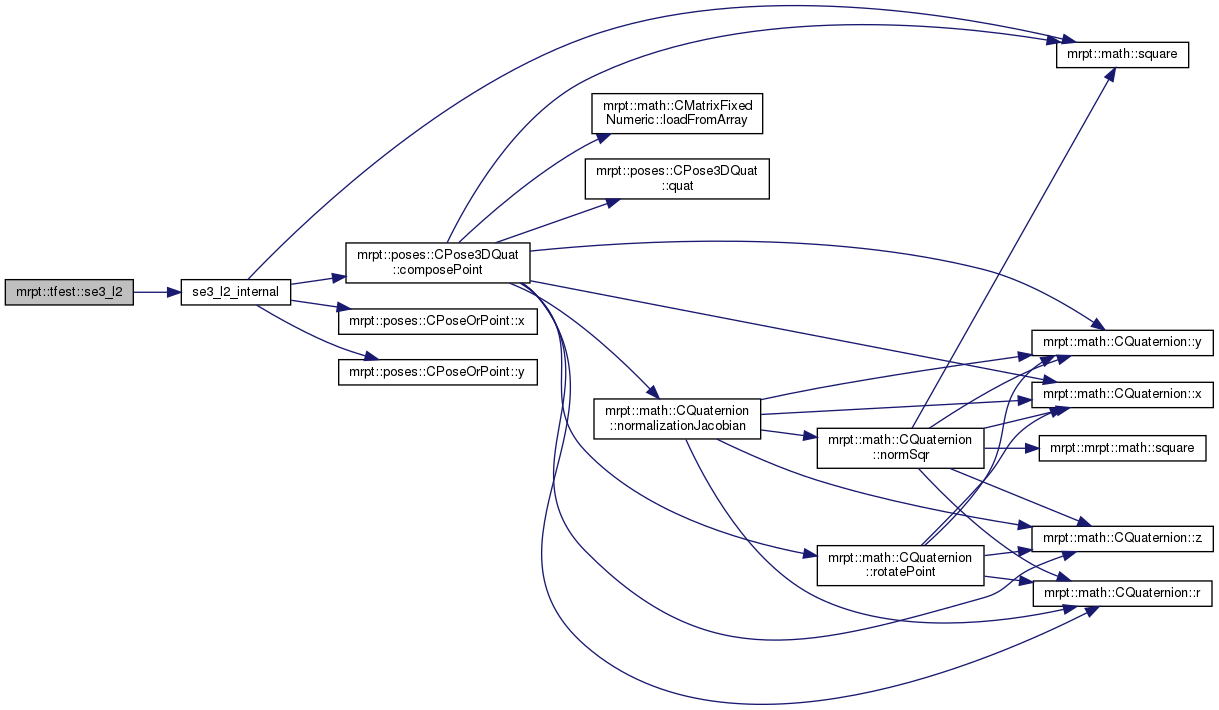
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.This version accepts corresponding points as two vectors of TPoint3D (must have identical length).
Definition at line 208 of file se3_l2.cpp.
References se3_l2_internal().

◆ se3_l2_robust()
| bool mrpt::tfest::se3_l2_robust | ( | const mrpt::utils::TMatchingPairList & | in_correspondences, |
| const TSE3RobustParams & | in_params, | ||
| TSE3RobustResult & | out_results | ||
| ) |
Least-squares (L2 norm) solution to finding the optimal SE(3) transform between two reference frames using RANSAC and the "quaternion" or Horn's method:
- "Closed-form solution of absolute orientation using unit quaternions", BKP Horn, Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1987.
The optimal transformation q fulfills 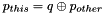 , that is, the transformation of frame
, that is, the transformation of frame other with respect to this.

- Parameters
-
[in] in_correspondences The set of correspondences. [in] in_params Method parameters (see docs for TSE3RobustParams) [out] out_results Results: transformation, scale, etc.
- Returns
- True if the minimum number of correspondences was found, false otherwise.
- Note
- Implemented by FAMD, 2008. Re-factored by JLBC, 2015.
- [New in MRPT 1.3.0] This function replaces mrpt::scanmatching::leastSquareErrorRigidTransformation6DRANSAC()
Definition at line 32 of file se3_l2_ransac.cpp.
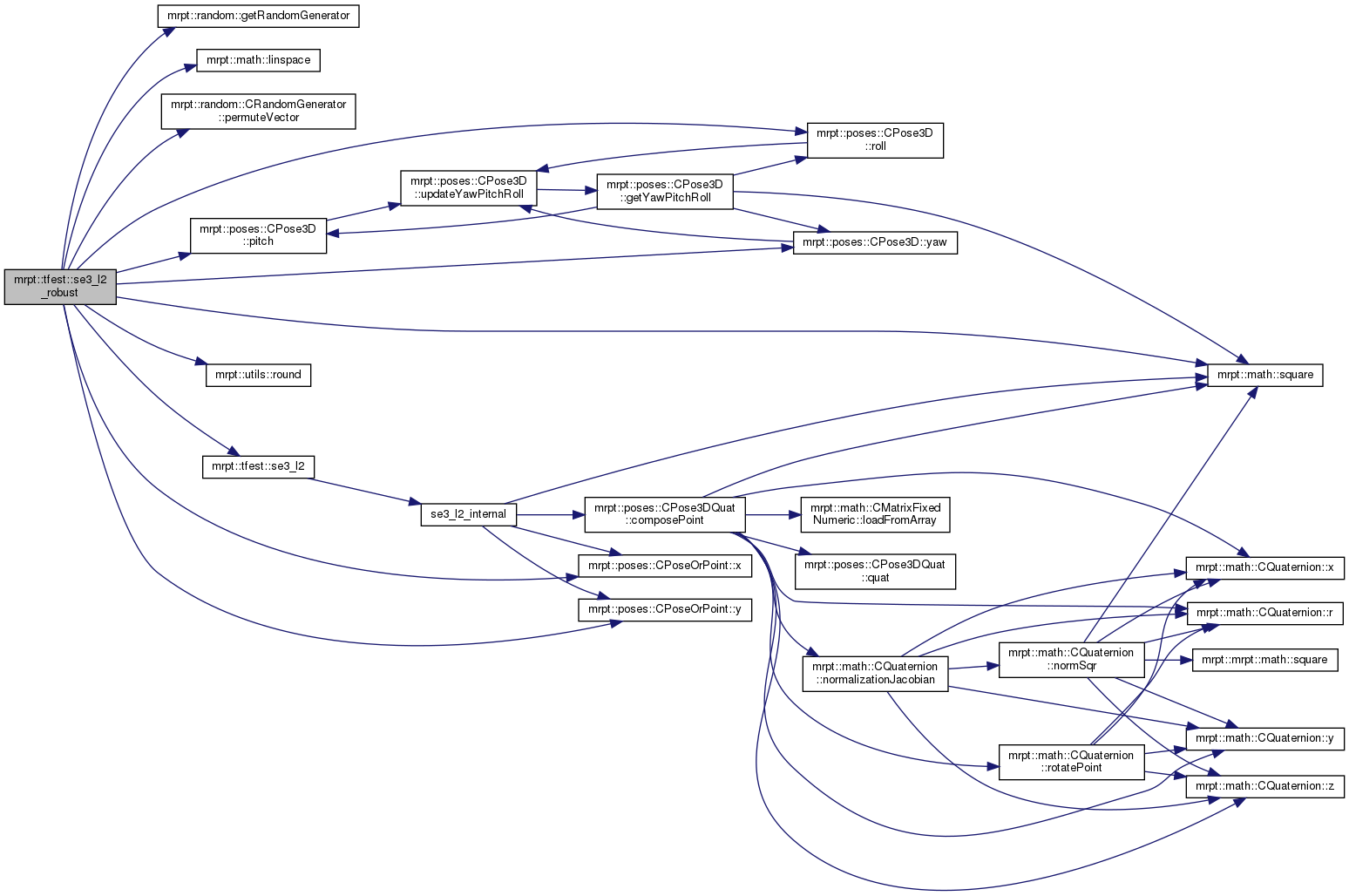
References ASSERTMSG_, mrpt::random::getRandomGenerator(), mrpt::tfest::TPotentialMatch::idx_other, mrpt::tfest::TPotentialMatch::idx_this, mrpt::tfest::TSE3RobustResult::inliers_idx, mrpt::math::linspace(), MRPT_END, MRPT_START, mrpt::random::CRandomGenerator::permuteVector(), mrpt::poses::CPose3D::pitch(), mrpt::poses::CPose3D::roll(), mrpt::utils::round(), mrpt::tfest::TSE3RobustResult::scale, mrpt::tfest::se3_l2(), mrpt::math::square(), mrpt::tfest::TSE3RobustResult::transformation, mrpt::poses::CPoseOrPoint< DERIVEDCLASS >::x(), mrpt::poses::CPoseOrPoint< DERIVEDCLASS >::y(), and mrpt::poses::CPose3D::yaw().
Referenced by TEST().